Molecular Weight Measurement of Glycoproteins Using a Benchtop MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometer
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometers are a mass spectrometer type that is used in a wide range of fields likewise LCMS, in terms of high through-put and high sensitivity. These instruments are being utilized more and more for simple molecular weight measurement and profiling of synthesized products and high-molecular compounds. This is because instruments of this type have several features: singly-charged ions are generated so molecular weights can be recognized easily, the applicable mass range is wide, and there are many solvent options because the sample is dried before measurement.
On the other hand, due to changes in social conditions in these several years, government offices and private enterprises strongly request the reduction of costs for both introduction and running of instruments used for such applications. The benchtop MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer "MALDI-8020" is a new instrument that can sufficiently meet such market needs. The noteworthy point of this instrument is that it has a shorter flight tube, which is the key feature of its small size, while retaining the performance equal to or higher than that of a conventional model.
Molecular weight measurement of proteins modulated by post-translation modification using a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer is the most basic application in the fields of biochemistry and molecular biology. Molecular weights of glycoproteins, in particular, are observed as a molecular weight distribution of multiple components because they are heterogeneous due to the difference in their sugar chain structures.
This article introduces an example of measuring molecular weights of such glycoproteins using the benchtop MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer "MALDI-8020".
Example of Glycoprotein Molecular Weight Measurement
Fig. 1 shows the amino acid sequence of Ribonuclease B. It is known that due to the N-linked glycosylation of the high mannose type, this protein is detected with its main component being a modification approx. 1217 greater than its intrinsic mass. Bovine derived ribonuclease B (5 pmol) was mixed with ferulic acid (10 mg/mL, 50 % acetonitrile/0.1 % formic acid solution), and analyzed in linear mode using MALDI-8020. The result is shown in Fig. 2. The singly-charged protonated molecule of the detected ribonuclease B is detected at m/z 14890, which is consistent with the theoretical value (14899.3). In addition, the distribution due to heterogeneous sugar chains is detected as a mass difference (theoretical value: 162) derived from hexose. As indicated above, the resolving power, mass accuracy, etc., of the linear mode of the MALDI-8020 are comparable to those of a larger conventional MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer in the same mode.

Fig.1 Amino Acid Sequence and Glycosylation of Ribonuclease B
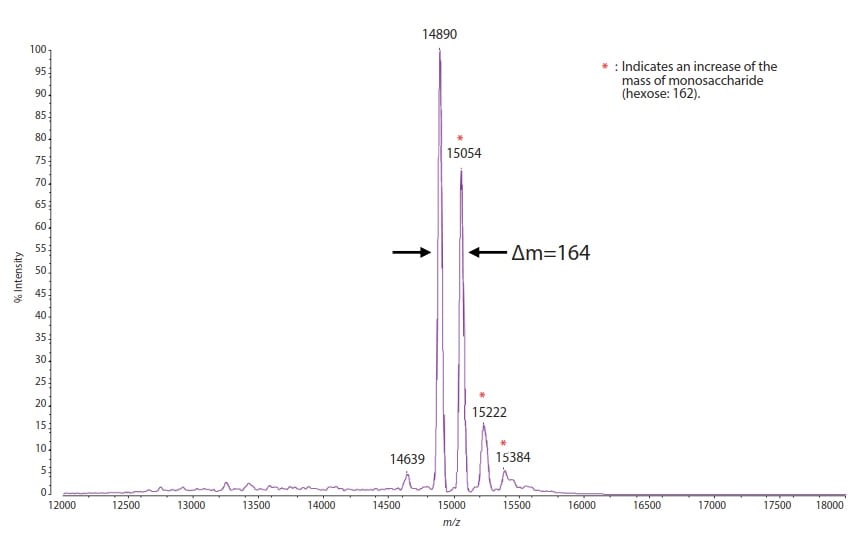
Fig.2 Mass Spectrum of Ribonuclease B
Benchtop MALDI-TOF MS "MALDI-8020"

Key features:
- Linear mode (positive ion) MALDI-TOF
- 200 Hz solid-state laser, 355 nm
- Load-lock chamber for fast sample introduction
- UV laser-based source cleaning (patented)
- Small footprint/benchtop design
- Quiet operation (<55 dB)


