Carbon Nanotube | Purity | Evaluation of Purity and Heat Resistance
Purity
Evaluation of Purity and Heat Resistance
When carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are heated in air, their mass reduces due to combustion. This mass reduction can be used to evaluate the purity of CNTs. The decomposition temperature can also be used to evaluate the heat resistance of CNTs, and this is applied to investigating the conditions of CNT formation.
The DTG-60 Thermal Analyzer simultaneously performs measurements of changes in mass and DTA measurements of the exothermic peak temperatures and calorific values, which allows detailed determination of the ratio of amorphous carbon and CNTs.
Fig. 1 shows the thermogravimetric (TG) curve and differential thermal analysis (DTA) curve of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) created by arc discharge. The largest exothermic peak in the DTA curve is near 683 ºC, which indicates the combustion of SWNTs. As the 322 ºC peak in the DTA curve is thought to be the combustion of amorphous carbon, the content ratio of SWNTs and amorphous carbon can be determined from their mass loss ratios in the TG curve.
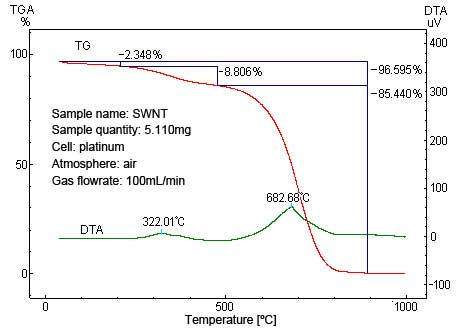
Fig. 1 TG/DTA Measurements (by DTG-60) of SWNTs Produced by Arc Discharge (Samples supplied by Ando Laboratory, Faculty of Science and Technology, Meijo University)



