SSG-H Series - Features
One-Touch, Strain Gauge Extensometers
1 µm Absolute Accuracy and 0.5% Relative Accuracy - Compliant with Plastic Tensile Test and Elastic Modulus Measurement Requirements of ISO 527, JIS K 7161, and ASTM D638
Plastic tensile test standards, represented by ISO 527, JIS K 7161, and ASTM D638, require highly accurate displacement measurements.
SSG-H series extensometers are compliant with the aforementioned plastic tensile testing standards and are used widely by plastics manufacturers, public testing institutions, and universities
ISO 527, JIS K 7161, and JIS K 7162 require:
- Extensometer elongation measurements with accuracy within ±1% of the measured value.
- Elastic modulus values based on a secant line or regression line between the two strain points of 0.0005 (0.05%) and 0.0025 (0.25%).
ASTM D638 requires:
- Tensile elasticity measurements with ASTM E83 Class B-2 accuracy (absolute accuracy of 10 m for a 50 mm gauge length and relative accuracy within 0.5%)
- Class C accuracy (absolute accuracy of 50 m for a 50 mm gauge length and relative accuracy within 1%) for elongation measurements after the yield point and less than 20% elongation
- Relative accuracy within 10% above 20% elongation
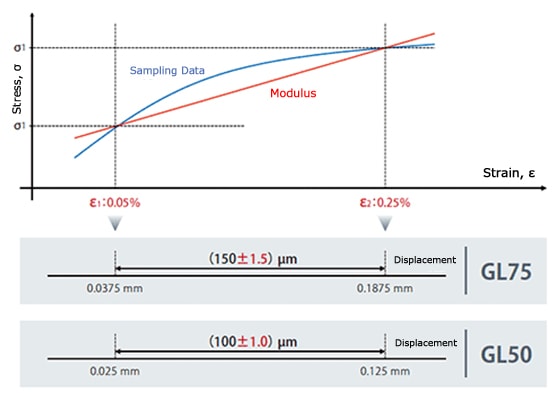
ISO 527, JIS K 7161, and JIS K 7162 Elastic Modulus Measurements
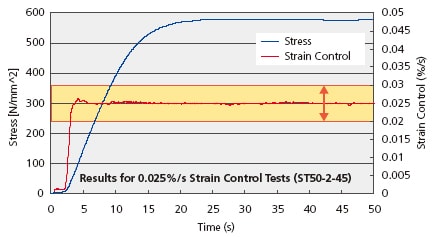
Satisfies Strain Control Requirements of ISO 6892 and JIS Z 2241
ISO 6892 and JIS Z 2241 detail test methods for determining the tensile strength of metallic materials. Included within these standards are two control methods for loading materials until they reach their yield point: a stress-rate controlled method and a constant strain-rate controlled method using an extensometer.
ISO 6891-1 defines the strain rate control method as Method A, where testing using this strain rate control method is expected to become increasingly common.
For strain-rate control testing according to ISO 6892 and JIS Z 2241, the SSG-H series extensometer is ideal.