Development of MRM Methods for Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies, or mAbs, have been used for over a decade in the treatment of a number of diseases but predominantly in the treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases. Quantifying therapeutic mAbs in biological samples has been traditionally addressed by ligand binding assays (LBA’s), however, there are major limitation in terms of extended method development times, reagent procurement, and matrix effects.
LC-MS/MS methods are emerging as an alternative approach to LBA’s and this paper describes the application of MRM methods to the quantitation of peptide fragments containing β-amyloid antibody (6E10) CDR’s (complementarity determining regions). CDR’s are targeted by LC-MS/MS as antibodies share a conserved sequence and are only differentiated by the three loops (CDR1-3) which are diverse and contain antibody specific peptides. By selectivity detecting CDR1-3 by LC-MS/MS helps to characterize and quantify disease specific antibodies isolated from patient sera or plasma and can be used to identify differing therapeutic agents.
Shimadzu LCMS-8050/8060 systems were used to identify CDR1-3 peptide fragments following a tryptic digest and Skyline software optimization1). The MRM method was set up to specifically detect peptide fragments containing β-amyloid antibody (6E10) CDRs.
Skyline was used to predict the peptide sequence for LC-MS/MS detection and also to optimize response for each precursor ion and product ion generated. The Skyline optimized MRM analysis method for CDR1-3 was then used to acquire highly specific and sensitive LC-MS/MS data.
1) Skyline is software developed by the MacCoss Lab of Biological Mass Spectrometry at the University of Washington.
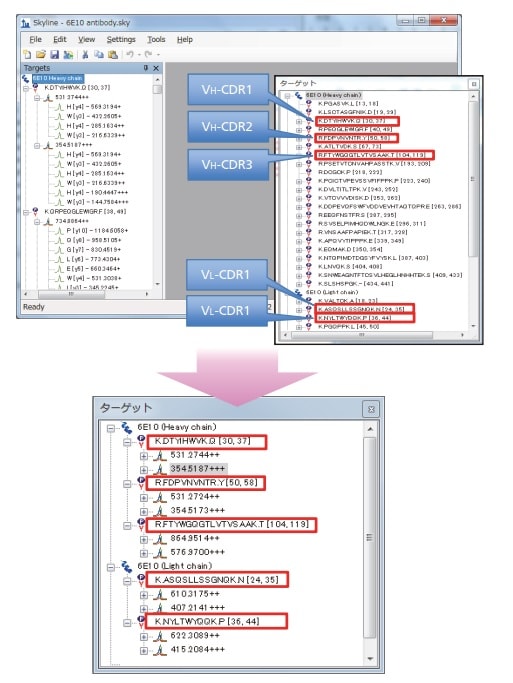
Fig. 1 Creating Analysis Methods Using Skyline (Selecting Trypsin Digestion Fragments Containing CDRs)
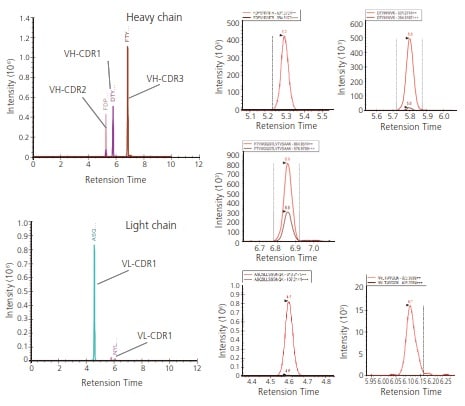
Fig. 2 Detection of Trypsin Fragments Containing CDR1-3 Using Standard Monoclonal Antibodies (6E10) Subjected to Trypsin Digestion (Data Analysis by Skyline)
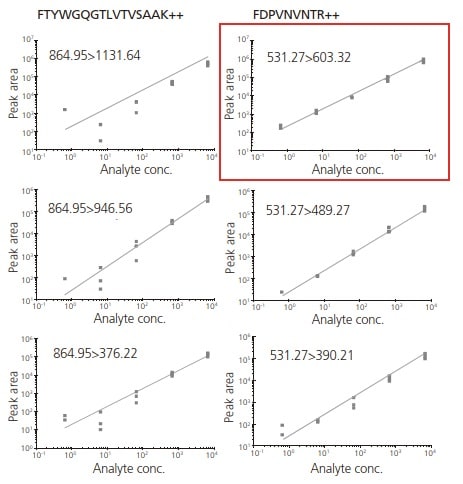
Fig. 3 Calibration Curve for Selected Peptides with Three Transitions.




