Characterization of Glycan Binding Site of O-Linked Glycopeptides Using MALDI-7090 High-Resolution MALDI-TOF MS
The majority of proteins synthesized in biological organisms undergo glycosylation. Glycosylation is modification with glycans of high structural heterogeneity composed of multiple monosaccharides, such as glucose and galactose, which are bonded together. These glycans classified into N-linked types and O-linked types. These types of glycan are known to play an important role in regulating protein function, and obtaining information on protein glycosylation is essential to the development of biopharmaceuticals.
One piece of this information related to glycosylation is where the glycan is bonded to the protein. Almost all N-linked glycans have an amino acid consensus sequence of -NXS/T-, which is used to discover potential N-linked glycan binding sites. N-linked glycan binding sites can be determined by digesting a glycoprotein with a protease, collecting glycopeptides from the digested material using lectin that binds specifically to glycans, cleaving the glycans from the peptides using the N-glycosidase (PNGase F) in the presence of H218O, labeling the N-linked glycan binding sites with a stable isotope, and then performing analysis.1) N-linked glycan binding sites can also be determined by MSn analysis using product ions that are specific to N-linked glycopeptides.2) The group of glycans called O-linked glycans are known to bond to a serine or threonine amino acid on the protein. Though often little information is available on the amino acid sequence around this O-linked glycan binding area, there is no enzyme suitable for cleaving the bond as with N-linked glycans, and also no specific product ions have yet been discovered, which makes determination of the binding site of O-linked glycans difficult.
In this article, we present a method for determining the O-linked glycan binding site that uses partial digestion with multiple enzymes and the MALDI-7090 high- resolution MALDI-TOF MS.
Partial Glycan Digestion with Glycosidases
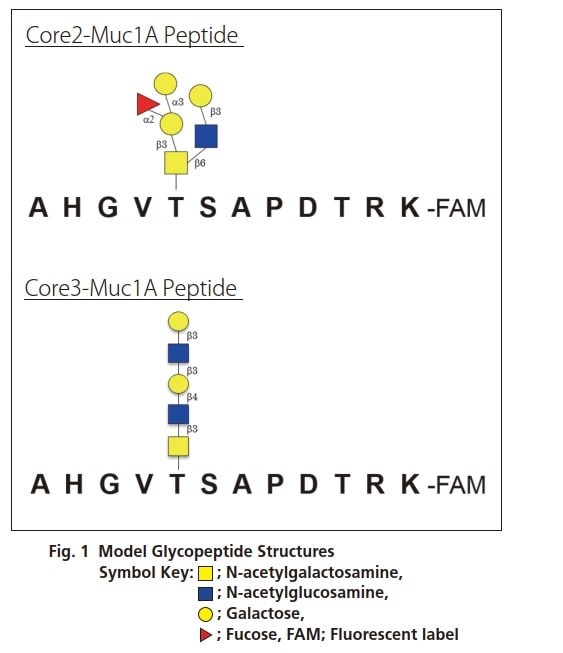
The O-linked FAM-labeled glycopeptides shown in Fig. 1 were used as model glycopeptides. This model glycopeptide (100 pmol) was added to the below cocktail of enzymes in buffer solution and reacted for 16 hours at 37 ˚C.

The glycopeptide before addition to the enzyme cocktail and the solution obtained after reaction with the above enzyme cocktail were subject to MS and MS/MS analysis using the MALDI-7090 system following desalination with a ZipTip µC18.
MALDI-7090

Key features:
- Market leading MS/MS resolution
- Proprietary solid state UV laser technology
- Ultra Fast acquisition speed in MS and MS/MS
- Integrated 10 plate loader
- Newly designed MALDI Solutions™ software


