Biomarker Searching | Analysis of Urine Samples Using the GC/MS Metabolite Component Database
Biomarker Searching
Analysis of Urine Samples Using the GC/MS Metabolite Component Database
■ GC/MS is occasionally used for the diagnosis of specific disease markers for inborn errors of metabolism.
The GC/MS Metabolite Component Database incorporates over 300 metabolites (amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids). Conducting parallel metabolic biomarker searches based on LC/MS and GC/MS achieves more comprehensive and complementary metabolite biomarker searches.
The components in urine samples were analyzed using the GC/MS Metabolite Component Database.
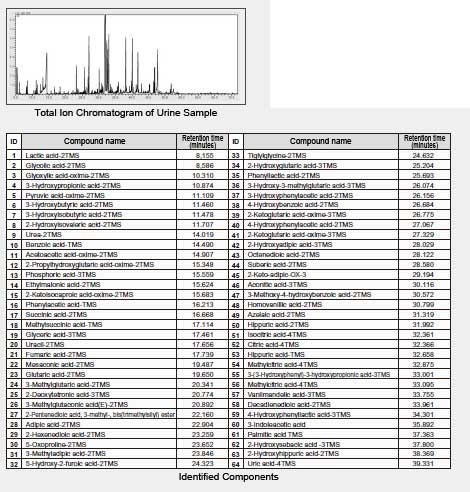
Metabolite component analysis by GC/MS requires sample pretreatment and derivatization. However, applying the established database reduces the workload of determining the analytical conditions for over 300 amino acid, fatty acid, and organic acid components and accelerates the detection and identification of candidate marker compounds.
The dedicated EZ: faast® derivatization pretreatment reagent kit can be used for amino acid analysis.
* EZ: faast® is manufactured by Phenomenex Inc. It is sold by Shimadzu GLC Ltd.
Metabolite Component Database

Retention indices, mass spectra, compound information (CAS numbers and structures), and method files for 311 metabolites (amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids) are registered in the database.
Since retention indices are registered in the database, analysis is possible by simply analyzing an n-alkane standard mixture and using the GCMSsolution Ver.2.5 AART (Automatic Adjustment of Retention Time) function, which supports the identification of compounds when no standard sample is available by accurately predicting retention times.
The analysis methods registered in the database reduce the effort to determine analytical conditions and perform actual sample analysis.
The analytical methods contain the appropriate data analysis conditions.


