Organophosphate Pesticides
From the viewpoint of separation, a capillary column is effective for the simultaneous analysis of organophosphate insecticides. Either an FPD or FTD can be used, but with its superior selectivity, an FPD is typically used for the analysis of organophosphate pesticides. The example below shows the analysis of commercially purchased onion spiked with 0.1 to 1.0 ng (absolute quantity) of 29 organophosphate pesticide components using a gas chromatograph (GC) with an FPD.
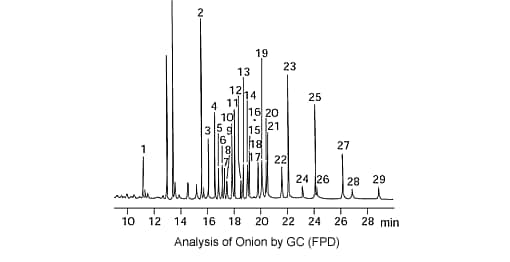
| Peak No. | Component Name | Peak No. | Component Name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dichlorvos (DDVP) | 16 | Parathion | |
| 2 | Salithion | 17 | α-CVP | |
| 3 | Dimethoate | 18 | β-CVP | |
| 4 | Cyanophos (CYAP) | 19 | Phenthoate | |
| 5 | Diazinon | 20 | Propaphos | |
| 6 | Disulfoton | 21 | Methidathion (DMTP) | |
| 7 | Formothion | 22 | Prothiofos | |
| 8 | Iprobenfos (IBP) | 23 | Isoxathion | |
| 9 | Dichlofenthion (ECP) | 24 | Ethion | |
| 10 | Methyl Parathion | 25 | Cyanofenphos (CYP) | |
| 11 | Chlorpyrifos-methyl | 26 | Edifenphos (EDDP) | |
| 12 | Fenitrothion (MEP) | 27 | Pyridaphenthion | |
| 13 | Malathion | 28 | EPN | |
| 14 | Fenthion | 29 | Phosalone | |
| 15 | Chlorpyrifos | |||
Gas Chromatograph (GC)

This separation/analysis instrument is widely used for the quantitative analysis of chemical substances. It is used with a detector and column combination that suits the analysis target components. Highly sensitive measurements are possible using the flame photometric detector (FPD), which is selective for phosphorous compounds.


