Mixed Polymer Sample as Microplastics using Pyrolysis GC/MS
As microplastics(MPs) analytical instruments, the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) is used in qualitative analysis of comparatively large MPs, while the FTIR microscope employing an infrared microscope is mainly used for fine MPs which cannot be analyzed by the attenuated total reflectance (ATR) method of FTIR. The FTIR microscope enables highly sensitive analysis of fine MPs with a size of approximately 10 μm.
However, in cases where it is difficult to distinguish the MPs containing multiple types of fine particles, it has been reported that the pyrolysis gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS) method is effective. Using Py-GC/MS method, qualitative analysis of individual polymers contained in mixed samples is possible by highly sensitive detection of the distinctive pyrolysis products of each polymer.
| Polymer | Pyrolysis product |
|---|---|
| PE | C20, alkane C20, α-alkene C20, α, w-alkene |
| PP | 2,4-dimethylhept-1-ene 2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1-undecene 2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1-undecene 2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1-undecene |
| PS | Styrene 3-butene-1,3-diyldibenzene 5-hexene-1,3,5-triyltribenzene |
| PVC | Benzene 1-Chloroindan Dihydronaphthalene Azulene |
Table 1 Pyrolysis Products and Analytical Conditions Used in Detection of Polymers
Fig. 1 shows the SIM chromatograms of the pyrolysis products of PE. By tracing the distinctive pyrolysis products of the respective polymers, the contents of the polymers could be specified accurately, even multiple polymers were intermixed in a sample.
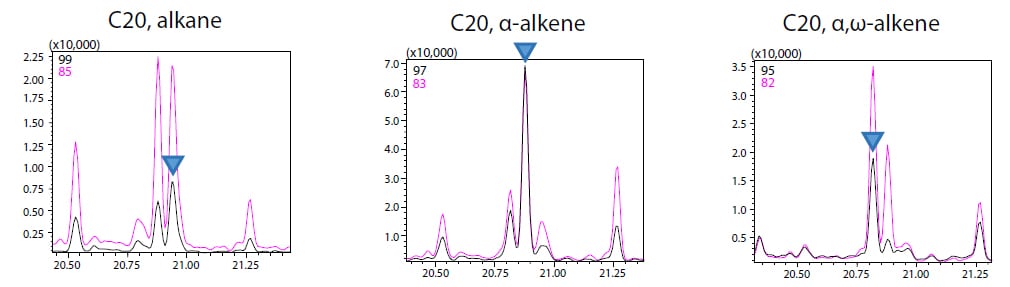
Fig. 1 SIM Chromatograms of Pyrolysis Products of PE in Mixed Polymer Sample



