Strength Test
Overview of Strength Test
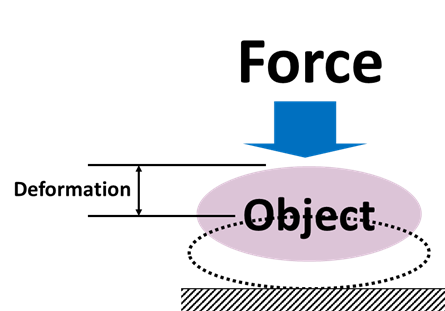
When a force is applied to an object, a strength test is performed to examine the characteristics of the object based on the relationship between the test force and the amount of deformation.
In the design and manufacture of machinery and buildings, it is important to understand their quantified properties by means of strength tests to ensure their safety.
Strength tests are performed at every stage of the process, from raw material to finished product, the purpose of which depends on the department responsible for the process. The quality control (QC) department conducts strength tests to ensure the incoming and outgoing materials, parts, and products meet manufacturing requirements. The test methods used for QC will follow standardized ISO, ASTM, and JIS methods, or company-developed standards for routine analysis. The research & development (R&D) department conducts strength tests to characterize the mechanical limits of materials and parts and to develop new materials and products. Unlike the lQC department, this department sometimes develops its own test methods and performs a variety of tests beyond routine analysis.
| QC and Manufacturing | R&D | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose |
|
|
| Work Characteristics |
|
|





