2-2) Decrease in Pressure
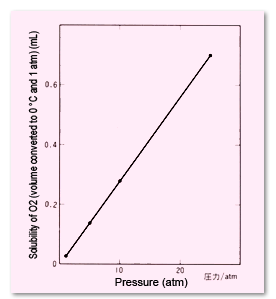
Fig. 3 Effects of Pressure (Partial Pressure) on Solubility of O2 in 1 mL Water (at 25 °C)
In general, the higher the gas pressure (partial pressure), the more the gas dissolves into a liquid (Figure 3). Conversely,if a gas at saturated solubility is at a high pressure, bubbles will form when the pressure is decreased.
Note: 1 atmosphere (1 atm) = 1.013 × 105 Pa






